2317. LCA offline (Easy)
Initially, there is a tree
consisting only of the root (vertex with the number 1). You must answer
the following queries:
·
ADD a b – hang the vertex b behind the vertex a (it is guaranteed that the vertex a already exists).
·
GET a b – return LCA of
vertices a and b.
Vertices are numbered
from 1 to n. We have one
tree at a time.
Input. The first line contains the
number of queries k. The next k lines contain the
queries themselves. It is guaranteed that the number of queries of each type
does not exceed 1000.
Output. For each query of the GET type,
print on a separate line one integer – the answer to it.
|
Sample input |
Sample output |
|
9 ADD 1 2 ADD 1 3 ADD 2 4 GET 1 3 GET 2 3 GET 3 4 ADD 2 5 GET 4 5 GET 5 5 |
1 1 1 2 5 |
SOLUTION
data structures – Least Common Ancestor
Algorithm analysis
The problem can be reduced to RMQ in O(n). RMQ preprocessing requires O(nlogn)
in time and memory. Executing a GET query takes O (1).
The problem can
also be solved with the
binary lifting method.
Example
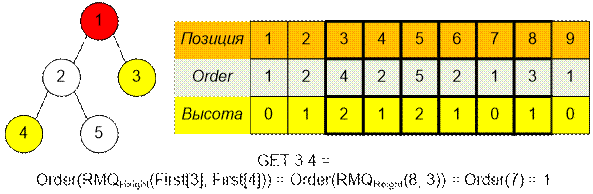
Let’s construct the tree given in example. Let’s run some queries.
The contents of the Height
array are the heights of the vertices:
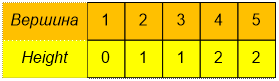
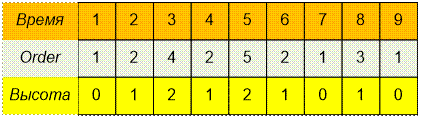
Массив порядка обхода вершин
Order с соответствующими им высотами:
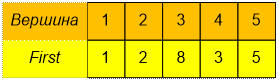
Содержимое массива First (First[i] содержит наименьший индекс, в котором в массиве Order стоит вершина i):
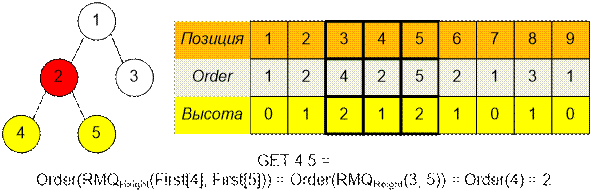
Выполним на
дереве несколько запросов.
Algorithm realization
Таблицу
RMQ будем строить в массиве mas. MAX – наибольшее возможное количество вершин в
дереве.
#define MAX 1010
#define LOGMAX 10
int mas[2*MAX][LOGMAX+1];
Дерево храним как граф в списке смежности g. Массивы Order, Height и First
используются для сведения задачи LCA к RMQ. Все поступающие запросы поместим в
массив пар Query.
vector<vector<int> > g;
vector<int> Order, used, Height, First;
vector<pair<int,int> >
Query;
int *hRMQ;
По массиву a размера size
строим массив mas, для которого
mas[i][j] = arg min(ai, ai+1, …, ai+2^j-1)
void
BuildRMQ(int *a, int
size)
{
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i
<= size; i++) mas[i][0] = i;
for (j = 1; 1
<< j <= size; j++)
for (i = 1;
i + (1 << j) - 1 <= size; i++)
if
(a[mas[i][j - 1]] < a[mas[i + (1 << (j - 1))][j - 1]])
mas[i][j] = mas[i][j - 1];
else
mas[i][j] = mas[i + (1 << (j - 1))][j - 1];
}
Функция RMQ возвращает минимум на
отрезке (ai, ai+1, …, aj) за O(1).
int
RMQ(int i, int
j)
{
if (i > j)
swap(i,j);
int k = 0;
while ((1
<< (k + 1)) <= j - i + 1) k++;
int res =
mas[i][k];
if
(hRMQ[mas[j - (1<<k) + 1][k]] < hRMQ[res])
res = mas[j - (1<<k) + 1][k];
return res;
}
Обход дерева в глубину. Порядок обхода вершин дерева (с фиксированием времени захода в вершину и возвращения в нее) сохраняем в массиве Order, их высоты – в массиве Height. Вызов dfs(v, h)
означает, что стартует поиск в глубину из вершины v, имеющей высоту h.
void
dfs(int v, int
h = 0)
{
used[v] = 1;
Order.push_back(v);
Height[v] = h;
for(int i = 0; i < g[v].size(); i++)
{
int to =
g[v][i];
if
(!used[to])
{
dfs(to, h + 1);
Order.push_back(v);
}
}
}
Препроцессинг LCA. Запускаем обход дерева в глубину.
Построение вспомогательных массивов. Выполняем препроцессинг RMQ по массиву
hRMQ, который содержит высоты последовательности вершин.
void
Init_LCA(void)
{
Order.push_back(0);
used.assign(MAX,0); Height.assign(MAX,0);
First.assign(MAX,0);
dfs(1);
First[i]
содержит момент времени, в который обход в глубину впервые заходит в вершину i.
for(int i = 1; i < Order.size(); i++)
if
(!First[Order[i]]) First[Order[i]] = i;
hRMQ = new int[Order.size()];
hRMQ[0] = 0;
for(int i = 1; i < Order.size(); i++)
hRMQ[i] = Height[Order[i]];
BuildRMQ(hRMQ, Order.size());
}
Функция LCA возвращает вершину
дерева, являющуюся LCA(i, j).
int
LCA(int i, int
j)
{
int index =
RMQ(First[i],First[j]);
return
Order[index];
}
Основная часть программы. Читаем входное дерево, заполняем
структуру g. Запросы собираем в массив пар Query.
scanf("%d\n",&k);
g.assign(MAX,vector<int>());
for(i
= 0; i < k; i++)
{
scanf("%s %d
%d\n",op, &a,&b);
if (op[0] == 'A') {g[a].push_back(b); g[b].push_back(a);}
else
Query.push_back(make_pair(a,b));
}
Сводим задачу LCA к RMQ.
Init_LCA();
Последовательно обрабатываем
запросы. Выводим ответ на каждый из них за O(1).
for(i
= 0; i < Query.size(); i++)
printf("%d\n",LCA(Query[i].first,Query[i].second));
Удаляем из памяти динамический
массив.
delete[] hRMQ;
Algorithm realization – binary lifting
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int n, l, a, b, i, res;
Store the tree in the adjacency list g. Declare timestamps arrays d and f when traversing the tree with dfs.
Declare an auxiliary array of ancestors up.
vector<vector<int> > g;
vector<int> d, f;
int time;
vector<vector<int> > up;
vector<pair<int, int> > Query;
char op[20];
Start
the depth first search from the vertex v.
The ancestor of v is the vertex p. Let the root of the tree be the
vertex with number 1.
void dfs(int v, int p = 1)
{
int i, to;
d[v] = time++;
The immediate
ancestor of v is p.
up[v][0] = p;
To
find the 2i-th ancestor of
the vertex v, first find the 2i-1-th ancestor of
the vertex v, that equals to x = up[v][i – 1]. Then find the 2i-1 -th ancestor
of the vertex x, that equals to
up[v][i] = up[x][i – 1] = up[up[v][i
– 1] ][i – 1]
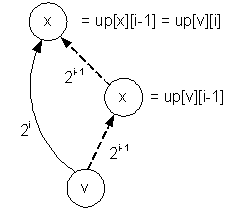
for (i = 1; i <=
l; i++)
up[v][i] = up[up[v][i - 1]][i - 1];
Continue
dfs. Iterate over the
vertices to, that can be reached
from v.
for (i = 0; i <
g[v].size(); i++)
{
to = g[v][i];
If to is not an
ancestor of v, then continue the
search from the vertex to.
if (to != p) dfs(to, v);
}
f[v] = time++;
}
The function Parent returns 1 if a is the ancestor of b.
int Parent(int a, int b)
{
return (d[a] <= d[b]) && (f[a] >= f[b]);
}
Function
LCA
returns the least common ancestor of the vertices a and b.
int LCA(int a, int b)
{
if (Parent(a, b)) return a;
if (Parent(b, a)) return b;
for (int i = l; i >=
0; i--)
if (!Parent(up[a][i], b)) a = up[a][i];
return up[a][0];
}
The main part of the program. Read the input
data.
scanf("%d", &n);
g.resize(n + 1);
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
scanf("%s %d
%d\n", op, &a, &b);
For the
case of ADD
query, add an edge to the tree. When a GET query is made, save
its parameters in the Query array.
if (op[0] == 'A') { g[a].push_back(b); g[b].push_back(a); }
else
Query.push_back(make_pair(a, b));
}
d.resize(n + 1); f.resize(n + 1); up.resize(n + 1);
Compute l = ![]() . Initialize
an array up.
. Initialize
an array up.
l = 1;
while ((1 << l) <= n + 1)
l++;
for (i = 0; i <= n; i++) up[i].resize(l + 1);
Run the
depth first search from the vertex 1.
dfs(1);
Compute
and print the answers for the queries of type GET.
for (i = 0; i < Query.size(); i++)
printf("%d\n", LCA(Query[i].first, Query[i].second));

